Cyber threats are evolving at an alarming pace, pushing businesses and individuals to seek smarter, more secure ways to safeguard sensitive information. Biometric security has emerged as a game-changer, offering authentication methods that are as unique as the individuals they protect. Instead of relying on passwords that can be guessed, stolen, or forgotten, biometric security leverages physical traits, something that’s inherently yours and nearly impossible to replicate.
What is biometric security?
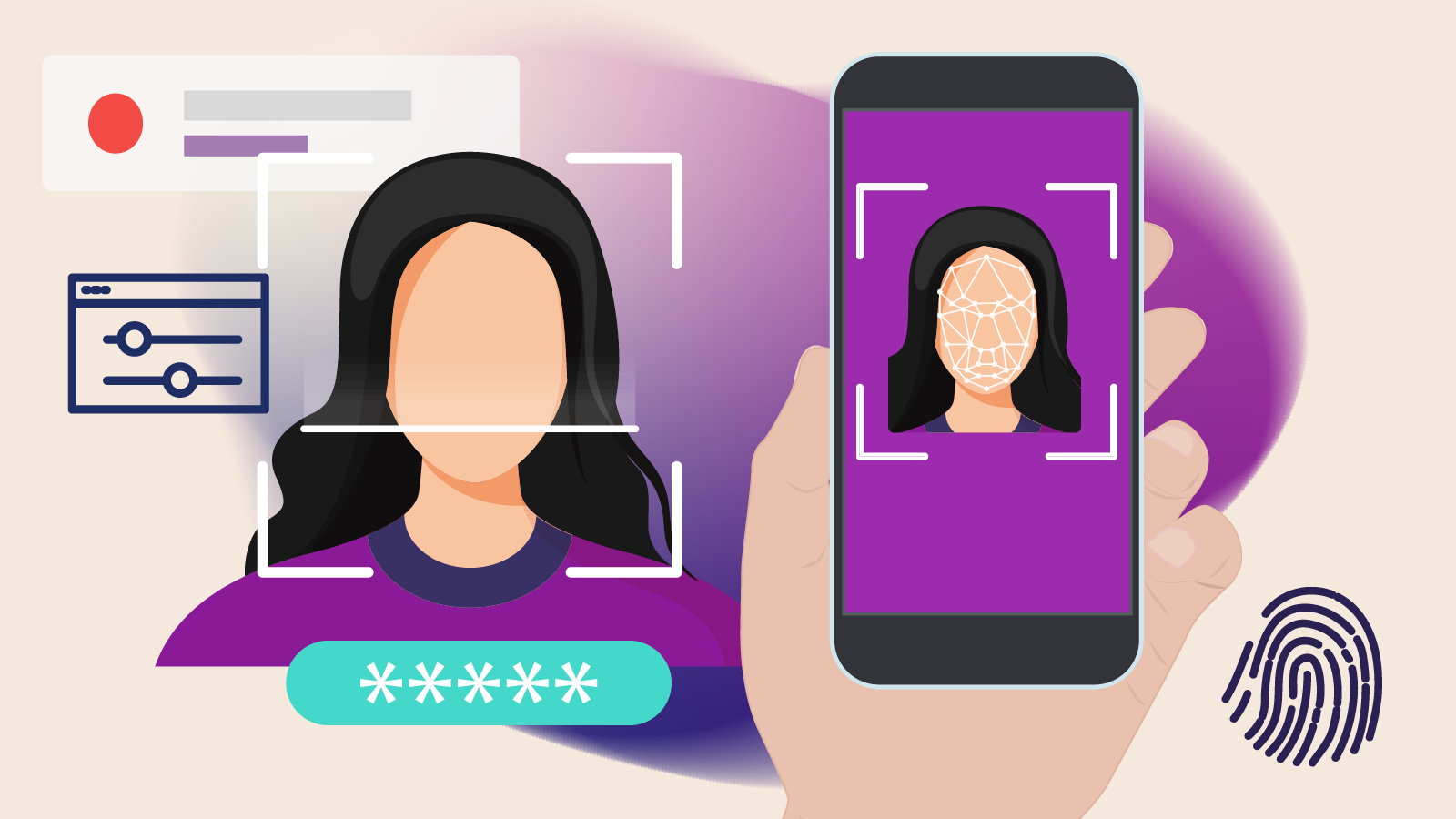
Biometric security uses distinct biological characteristics to verify identity, making authentication both seamless and highly secure. This is what you use when you unlock your device or access a restricted area simply by using your fingerprint, face, or voice. Unlike passwords or keycards, these personal identifiers cannot be misplaced or easily compromised.

How biometric authentication works
At its core, biometric authentication follows a sophisticated yet straightforward process:
- Enrolment: Your biological trait—such as a fingerprint or facial scan—is initially captured and converted into a secure digital template.
- Conversion: This template is transformed into a complex, encrypted data set for storage.
- Authentication: When access is requested, a new scan is taken and compared against the stored template to verify identity.
Biometric systems commonly utilise:
- Fingerprint recognition – A widely used method in smartphones and workplace security.
- Facial mapping – A growing standard in mobile technology and border control.
- Iris scanning – A highly accurate method favoured in high-security environments.
- Voice pattern analysis – A contactless option for authentication via phone or smart assistants.
Why businesses are embracing biometric security
The appeal of biometric security lies in its multiple advantages:
- Unparalleled security: Biometric traits are unique to each person, making them incredibly difficult to forge or steal.
- Convenience: No more struggling with forgotten passwords or cumbersome authentication steps.
- Fraud reduction: Cyber criminals face significant barriers when attempting to impersonate someone.
- Regulatory compliance: Many industries now require advanced authentication methods to meet stringent data protection laws.
However, while biometric security is a powerful tool, it’s not without its challenges. Privacy concerns remain a major issue, as the collection and storage of biometric data raise valid questions about misuse and potential breaches. Additionally, technological limitations can result in errors, especially in cases of poor lighting, changes in appearance, or hardware malfunctions. High implementation costs present another hurdle, as deploying and maintaining biometric systems can be expensive, particularly for small businesses. Perhaps the most concerning challenge is the irreversible nature of biometric data breaches. Unlike passwords, which can be reset, biometric identifiers cannot be changed once compromised.
Real-life biometric security impact
Biometric authentication is already widely used in everyday life, including:
- Smartphone unlocking: A mainstream feature on most modern devices.
- Workplace access control: Used in offices and secure facilities.
- Financial transactions: Banks and payment services are integrating biometric authentication for secure transactions.
- Government security protocols: Border control, national ID programs, and law enforcement rely heavily on biometric verification.
The future of biometric security
Biometric security is far from static. It continues to evolve, bringing innovations that could redefine authentication.
Multi-factor biometric authentication is one such advancement, combining multiple biometric factors, such as face and voice recognition, to enhance security.
Behavioural biometrics is another emerging trend. It analyses patterns like typing speed, mouse movements, and other unique behaviours to add an extra layer of authentication.
Additionally, AI-powered recognition systems are making biometric authentication more accurate and secure, minimising false positives and improving overall reliability.
These innovations are shaping the future of digital identity, pushing security beyond traditional methods and making authentication both smarter and safer.